Augmented Reality Support for Interventional Radiology
Medical Templates and ETH Zurich are enhancing the Cube Navigation System with augmented reality to improve precision in radiological interventions. A recent study shows significant improvements in training outcomes and user satisfaction with this new AR application.
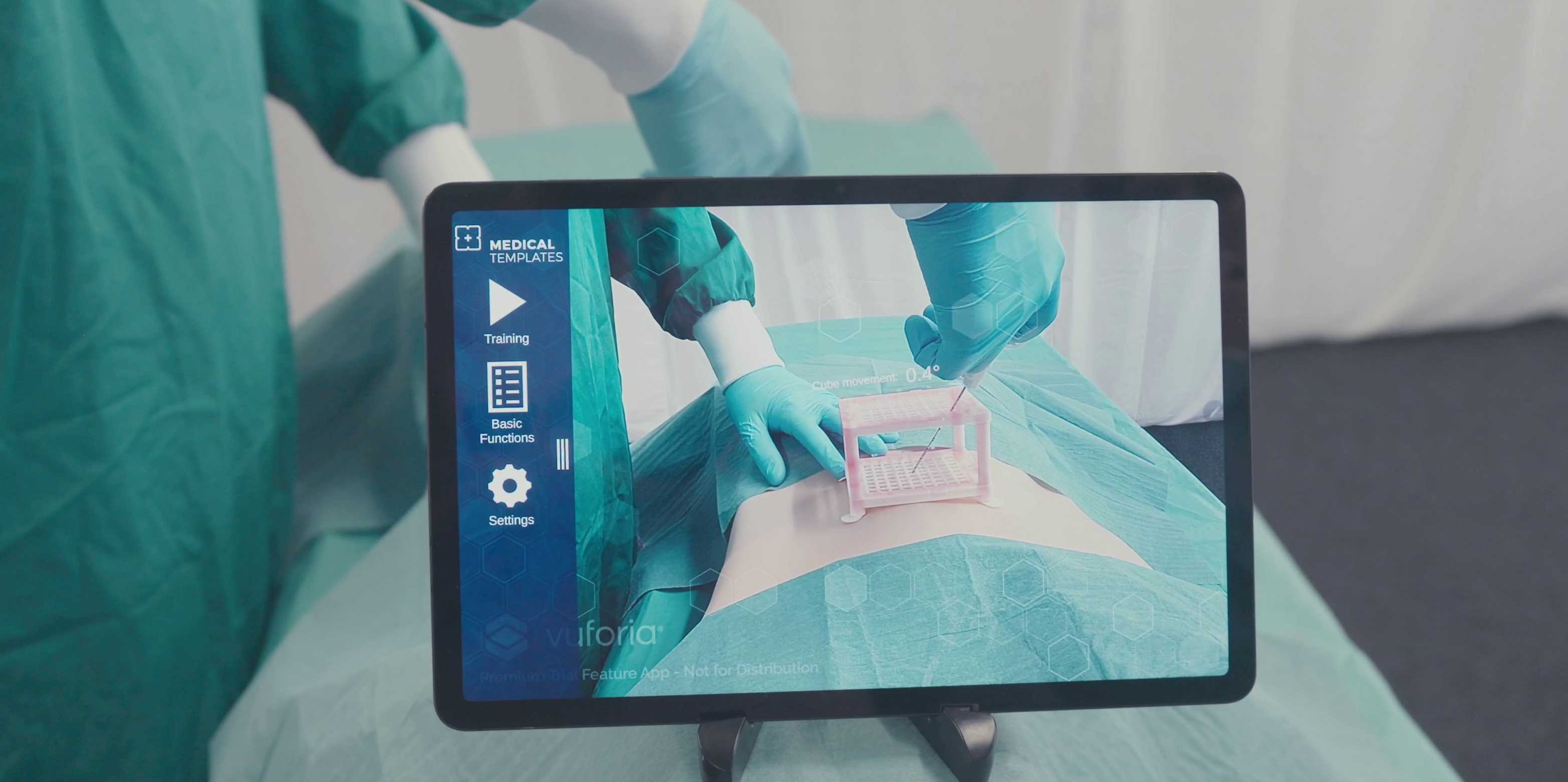
The Swiss start-up Medical Templates has successfully launched its Cube Navigation System (CNS), a straightforward solution for guidance in radiological needle interventions. The system, which now has FDA clearance, is increasingly being adopted by healthcare providers. Building on this success, Medical Templates, in collaboration with the product development group at ETH Zurich, is driving innovation further through the integration of augmented reality (AR) technology. Supported by the Swiss Innovation Promotion Agency Innosuisse, this joint effort aims to enhance the functionalities and usability of the existing CNS system, with the goal of improving precision, efficiency, and patient safety in radiology.
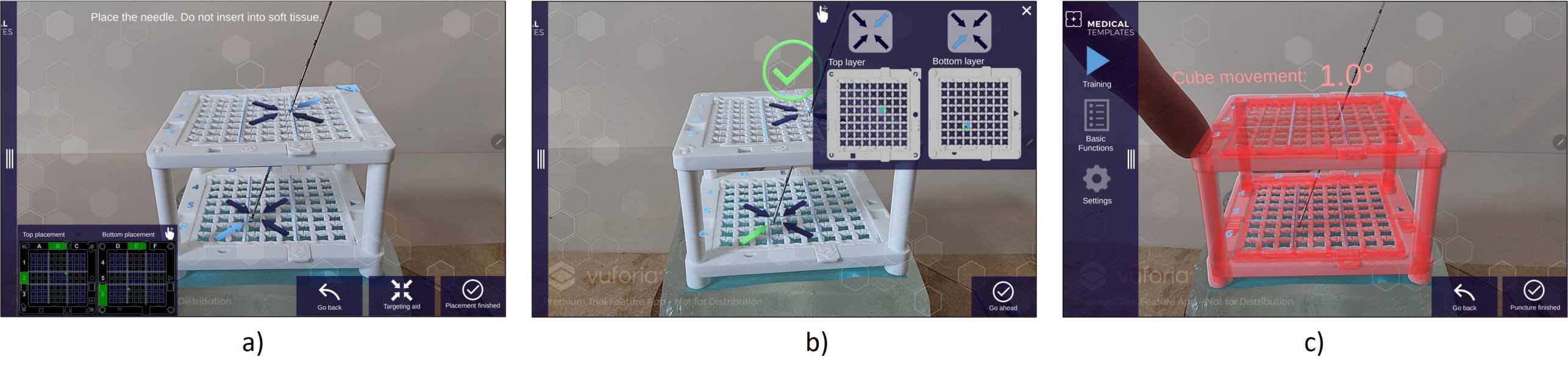
The newly developed AR tablet application enhances the capabilities of the Cube Navigation System by providing an intuitive, interactive interface that guides clinicians through complex procedures. This system features a closed-loop approach designed to improve accuracy through a combination of advanced tools. These features provide radiologists with better control and confidence during interventions:
a) Holographic displays for precise guidance
b) Deep-learning algorithms for verifying needle placement
c) Alert systems to indicate trajectory deviations
Medical Templates and ETH Zurich conducted a study to test the AR functionalities within a training application. The study compared traditional training approaches to the AR-based method using a cohort of 34 medical students. The participants were divided into two groups: one trained using the AR application, while the other followed conventional instructional methods. The findings demonstrated a clear advantage for AR-based training, with participants showing a 55.1% reduction in missed target coordinates and a 35.1% reduction in unintended needle trajectory deviations compared to those trained with conventional methods. The AR group also reported significantly higher user satisfaction. These results underscore the potential of AR to significantly improve training efficacy, ultimately enhancing the safety and precision of percutaneous interventions.
Looking ahead, Medical Templates and ETH Zurich are committed to further expanding the capabilities of spatial computing in medical applications. Aiming to integrate AR head-mounted displays and extend the use of augmented reality to cover the entire workflow of percutaneous image-guided needle placement. By incorporating AR into each step of the intervention process, the procedural efficiency and patient safety is supposed to be further improved. This continued innovation promises to strengthen the effectiveness of the Cube Navigation System, advancing the standards of precision in radiology and clinical practice.