Performance Assessment of Physicians
One key challenge in simulation-based training of cardiovascular interventions is the performance assessment of operators. Traditionally, this assessment is conducted by experts and thus is highly subjective. We are utilizing two technologies, mobile eye tracking and pose estimation algorithms, to address this issue and to provide objective assessment tools for better evaluation of surgical tasks during real cardiovascular interventions. Ultimately, these objective assessment tools enable us to improve the quality of training and could potentially be used to guide procedures and improve operator performance and patient safety.
The following projects are financed by and conducted in close collaboration with Prof. Maisano from the USZ.
Mobile Eye Tracking (Human Behavior)
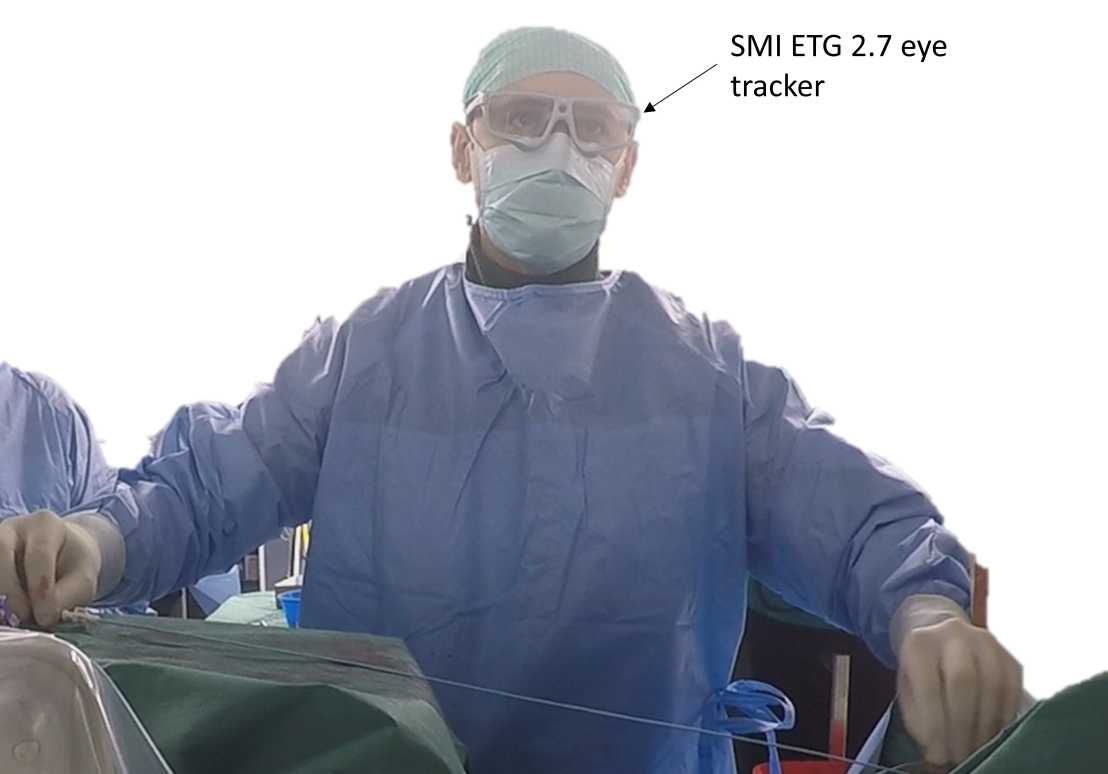
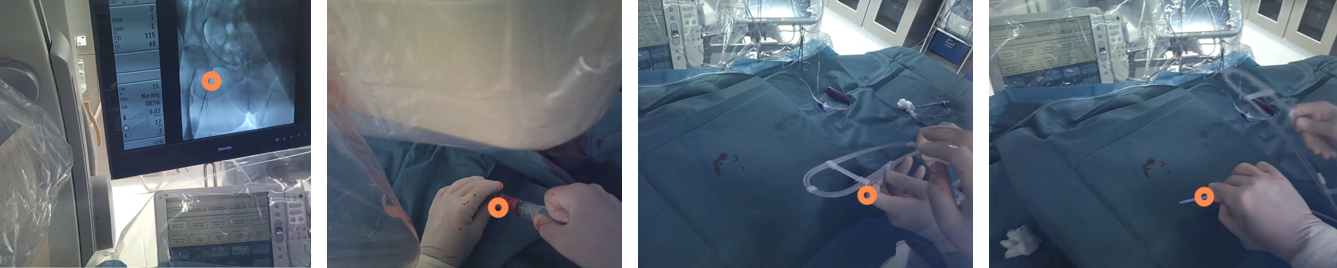
Operators from the USZ performed real-life cardiovascular interventions, while wearing eye tracking glasses. To date we analyzed 35 procedures and were able to identify clear visual behavior patterns exhibited by the operators. Furthermore, we were able to show that the viewing strategies of the experts differ from the strategies of the novice operators. By exploiting these differences we can assess the skill level of operators based on eye tracking data.
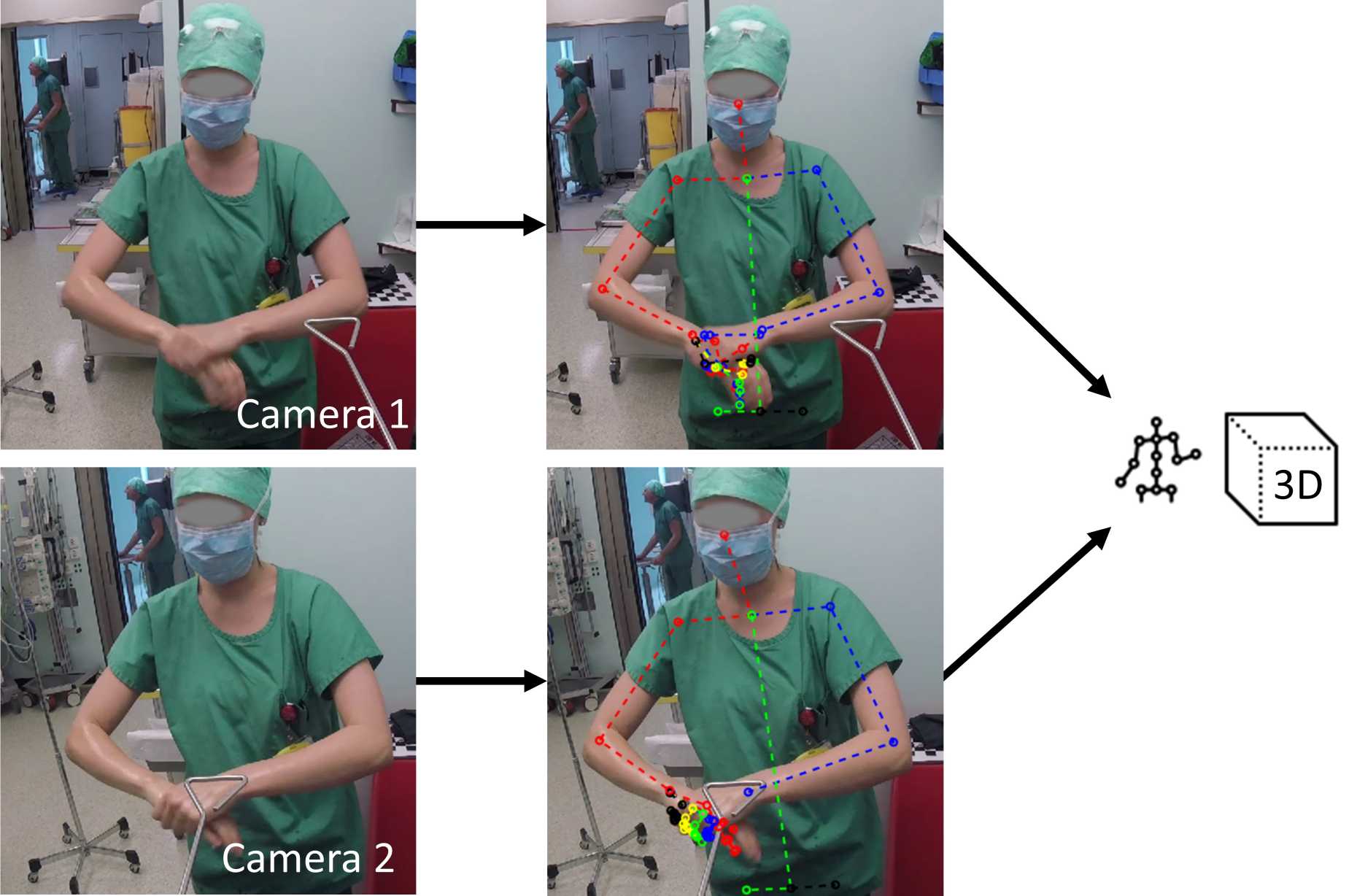
Pose Estimation
We are using pose estimation technology such as external page OpenPose to objectively measure the performance and skill of operators. With our stereo camera setup, we can detect and track the operators motion during real-life cardiovascular interventions. In combination with standard operating protocols, we can for example measure if the operators adhere to the protocols or if they deviate from it. This allows as to objectively measure their performance.